Knowing the
properties of ferrite magnets
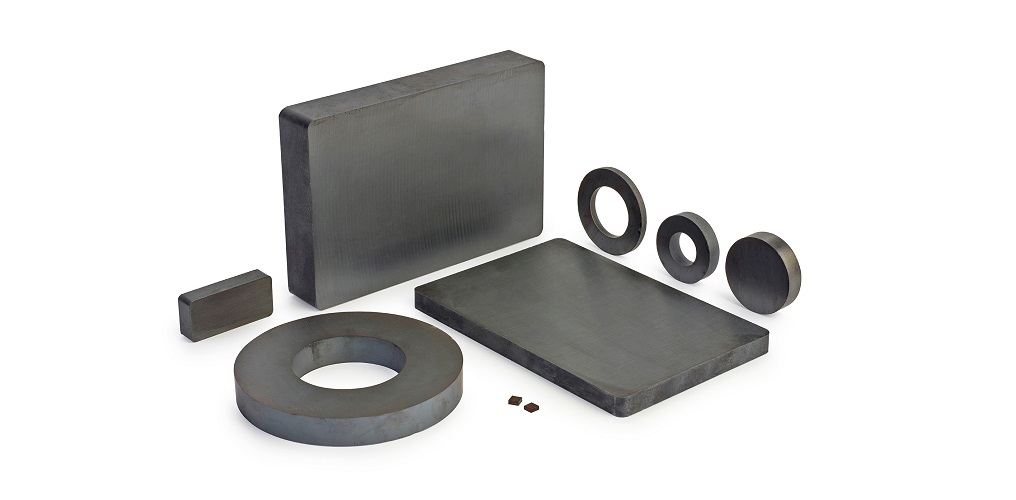
Ferrite Magnets and all their properties
Ferrite magnets are permanently attached and
have good mechanical properties that allow them to be cut into different shapes
and sizes. These magnets are cut with diamond tools, while standard drills and
wire spark erosion techniques do not work because they are electrically
insulating.
This occurs because the current does not pass
through them due to their extremely high electrical resistance, characteristic
from which they are known by their other name: ceramic magnets.
Ferrite magnets are manufactured by wet or dry
pressing and sometimes by extrusion. Wet pressing provides stronger magnetic
properties, e.g. C8 ferrite. Dry pressing provides better dimensional
tolerances, such as C5 ferrite.
In addition, the magnets are sintered to fuse
the powder and then processed to the final shape. The extrusion method can be
applied to produce arc segment shapes that are then cut lengthwise. Sometimes
new tools are required to produce ferrite magnets if existing tools do not
allow the desired shape to be produced. Typical tolerances for ferrite magnets
are +/- 0.25 mm, although +/- 3% is also used.
Improve heat resistance
When ferrite magnets heat up, their high
intrinsic coercivity really improves (improving demagnetization resistance)
making them extremely popular in motor and generator designs.
In fact, the use of ferrite magnets in
loudspeaker applications is very common, precisely because only these types of
permanent magnets become noticeably more resistant to demagnetization when
heated.
Ferrite magnets have a positive temperature coefficient
of intrinsic coercivity (it changes in +0.27% / degrees C with respect to the
environment) and only ferrite expresses this characteristic that much. However,
the magnetic output drops with temperature (it has a negative induction
temperature coefficient of -0.2% / ambient degC). The end result is that
ferrite magnets, or ceramic magnets, can be used at high temperatures with very
few problems.
Ferrite magnets can be used up to +250 degrees
C (and in some cases up to +300 degrees C), making them ideal for use in
electrical machines and most high temperature applications. At sub-zero
temperatures, for example, less than -10 to -20 degrees Celsius, ferrite
magnets may begin to show reduced tensile strength. That is, the temperature
and degree of attenuation depends on the shape of the magnet and are
application specific. In most applications, the operating temperature is not
low enough for this effect to occur.
This is because if its temperature coefficient
of +0.27% / degrees C of intrinsic Coercivity - the Hci drops as the magnet
cools. The ferrite can demagnetize if placed in a too cold environment, but it
is the total design of the magnetic circuit that determines how cold the magnet
must be before any impairement is noticed.
Characteristics and uses of ferrite magnets
Among the main features of ferrite magnets is the fact that it is possible to cut them without losing magnetism, while they can be used in a number of applications, including:
If you have doubts between buying a neodymium magnet or ferrite magnets, at IMA we help you choose the type of magnet that best suits your needs. If you have any questions, please ask us.